Doubled Lifetime - Optimization of a Die Casting Slide
Facing the high quality and the high output requirements of die cast parts together with the high cost of die casting tooling, Dongguan Modern Metal Precision, P. R. China, started research on 3-D printed slide inserts.
For many products, a gradual aging of the insert surface leads to a reduction of local cooling in the casting. This effect led to shrinkage defects in the castings during production. The scrap rate after leakage tests reached 30%. In order to ensure the required casting quality, the slides often already had to be replaced after 20 to 30 thousand casting cycles, resulting in increased production costs.
Based on the analysis of MAGMASOFT® results, the objective was to achieve new cooling channel designs with the aim to improve the slide insert lifetime and to increase the efficiency of the current production.
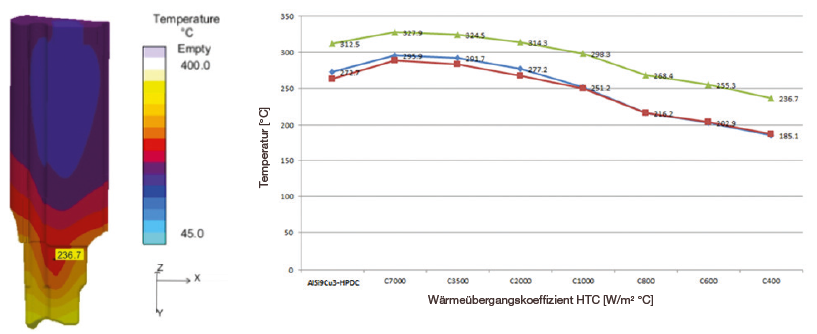
Under the assumption that the properties of the slide material remain constant, the heat transfer between the aged surface and the casting can be represented by the heat transfer coefficient (HTC). Different HTCs were defined between the slide and the casting, keeping all other conditions unchanged. The comparison of the temperature field of the slide shows that the reduction of the heat transfer coefficient leads to a reduced surface temperature of the insert.
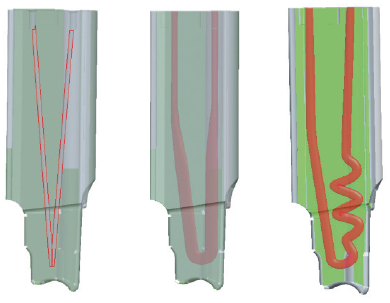
Using advanced 3-D printing technologies, the limitations of traditional CNC machining can be avoided. A faster cooling of the slide insert is ensured by a new type of channel design and through an increased cooling area of the cooling line.
Temperatures of the 3-D printed inserts are nearly 50°C lower than temperatures of the traditionally machined insert, also when considering a gradual aging of the insert (reduction of the heat transfer coefficient). This shows that the cooling effect of a 3-D printed insert is higher.
In practice, after adapting the 3-D printing technology for insert manufacturing, the casting quality was significantly improved and the shrinkage defects substantially reduced. The reject rate after leak tests was reduced to less than 2%. At the same time, the lifetime of the slide was improved to sustain up to 50 to 60 thousand casting cycles.
Based on MAGMASOFT® simulation results, the design of the mold cooling conditions could be accelerated to ensure the validity of the design.
Courtesy of Dongguan Modern Metal Precision Co., Ltd, P. R. China
MMP has been a successful manufacturer of aluminum die castings for the automotive industry since 2003.